![]()
CDNLAO Newsletter
No. 104, September 2024
![]()
In December 2019, the Korean government designated artificial intelligence (AI) technology as the key technology for the nation's future and announced the 'National AI Strategy.' In line with this government policy, the National Library for Children and Young Adults, Korea (NLCY) has been participating in the 'AI-Based Reading Activity Support Robot' research and development project since 2022. This project aims to foster children's interest in reading and allow them to experience AI sensitivity through interactive reading sessions with robots. This research, which is being conducted in three phases until 2024, involves six institutions: NLCY, Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology, Korea Culture Technology Institute, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Sogang University and Intflow.
In the first year, the project focused on developing core technologies for the reading support robot and service content. The second year aimed to enhance the robot technology, and the third year involves integrating the robot and service content, creating a prototype, and conducting test operations.
The main research areas are as follows:
- Development of children's speech recognition technology
- Development of emotion recognition technology based on voice and video
- Dialogue modeling
- Development of children's speech synthesis technology
- Development of motion control technology based on emotion expression
- Development of tactile behavior recognition technology using tactile sensors
- Collection of children's facial video and voice datasets
The design motif for the reading support robot 'PO-ME' is based on a Pomeranian, and its name is an acronym for Puppy robot, Optimistic, Motivating, and Encouraging.
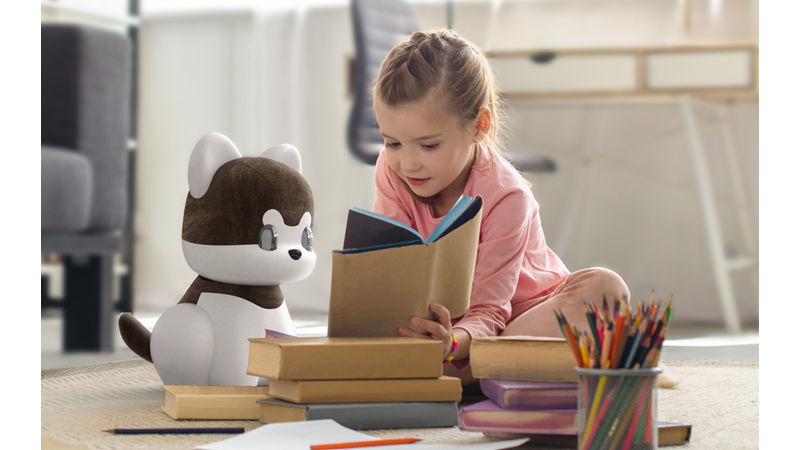

< AI Robot for Reading Support, PO-ME >
This year, the NLCY will conduct user studies with children aged 7 to 10 in three sessions:
- (1st session) July 20-21, 2024
- (2nd session) August 24-25, 2024
- (3rd session) October-November 2024 (tentative)
- Location: Children's Reading Room at the NLCY
- Participants: Children aged 7-10 (born 2014-2017)
- Activities: Experiencing the robot and confirming the relevance of the robot's emotional expression and interaction (each session takes approximately 20 minutes)
The first user study aims to confirm the positive impact of the social robot PO-ME on children's reading activities, particularly:
- Improving children's concentration and interest in reading when using the reading robot
- Assessing whether the intimacy with the robot positively contributes to reading activities
- Verifying touch interactions between the robot and children and collecting quantitative touch data to design the touch module
The second and third user studies will reflect feedback from the previous sessions to improve the PO-ME model and verify the positive impact on children's reading activities after implementing the feedback. The main target is children aged 7-10, with reading activity experiments conducted after a pre-questionnaire and interview, followed by post-experiment surveys and interviews. The secondary target is the children's guardians, who will also participate in an experiment after a pre-questionnaire and interview and post-questionnaires and interviews leading to the second experiment. The experiment method involves placing PO-ME in a reading environment where a child (one participant) conducts reading activities. Data will be collected through video and audio recordings to observe behaviors. After behavior observation, surveys and interviews will be conducted to apply feedback and collect further data.
Data to be collected includes:
- Concentration on the reading activity (reading time, reading concentration)
- Interest in the reading activity (interest in reading, reading comprehension)
- Robot-child rapport (rapport building time, presence of rapport)
- Robot touch (frequency, intensity, pattern)
- Robot interaction (interaction, usage patterns, recognition, appropriateness of emotional expression)
The results of the user studies will be crucial in determining the impact of the AI reading support robot PO-ME on children's reading concentration and interest and whether familiarity with the robot positively contributes to reading activities. Particularly, by analyzing the rapport formation process between children and the robot in detail, it is expected to improve the appropriateness of the robot's emotional expressions and interactions. This would help the reading support robot go beyond a mere auxiliary role, enabling children to participate in reading activities more joyfully and meaningfully.
Conclusion
AI technology not only opens up infinite possibilities for humanity but also revolutionizes the reading and learning experiences of children and adolescents. Through the AI-based reading activity support robot, the NLCY aims to provide enjoyable reading experiences to digital native children, fostering creative thinking and developing the competencies needed for future society. The NLCY is leading the learning environment in the digital age, striving to become a place where children can nurture their dreams and turn them into reality through creative learning. The NLCY will continue to support children and adolescents in moving toward a better future through ongoing technological innovation and program development.
Copyright (C) 2024 National Library for Children and Young Adults, Korea